Bootstrap theme
The Twitter Bootstrap framework is widely used for mobile-first responsive web applications. The Drupal Bootstrap bridge theme is one of several themes that brings this framework to Drupal. It looks good enough to be used on its own, but it can also be extended by means of sub-themes. You may use it either as a starter theme or as a base theme. This chapter will tell you how to set up and configure this theme and how to get started on sub-theming Bootstrap.
Table of contents
- Introduction
- Installation
- Creating a sub-theme
- Main menu
- Bootstrap GUI
- Layout
- Responsive layout
- Colours
- Bootstrap components and helper classes
- Inline form elements
- Updating Bootstrap
- Quirks
- Final word
Drupal projects discussed in this chapter: Bootstrap, jQuery Update.
Introduction
The Bootstrap framework was developed in 2011 by a small team lead by Twitter developers Mark Otto and Jacob Thornton. It is a a powerful mobile first front-end framework for faster and easier web development.
 The
Twitter Bootstrap framework is widely used for
mobile-first responsive web applications. There are good
reasons for that, as Christopher Gimmer explains
in Top 5 Reasons to use Bootstrap.
However, the Bootstrap framework is not
without its faults, and Ian Carrico argues that You Don't Need Bootstrap.
Read both sides of the argument and make up your own mind.
The
Twitter Bootstrap framework is widely used for
mobile-first responsive web applications. There are good
reasons for that, as Christopher Gimmer explains
in Top 5 Reasons to use Bootstrap.
However, the Bootstrap framework is not
without its faults, and Ian Carrico argues that You Don't Need Bootstrap.
Read both sides of the argument and make up your own mind.
Several adaptions for Drupal of the Bootstrap framework for Drupal exist and can be downloaded from Drupal.org. Most of these (see for example Bootstrap Business) are full-featured themes that just incorporate elements from Twitter Bootstrap in their design.
This chapter is about the Drupal theme project named just Bootstrap. The main purpose of this theme is to provide the scaffolding to allow developers to leverage of the Bootstrap 3 framework as a starter or base theme for a responsive sub-theme. However it also can also stand on its own.
Features of Drupal Bootstrap bridge theme:
- Based upon the Bootstrap 3 framework.
- 3-columns, 2-columns and 1-column layout.
- 8 block regions.
- Responsive (mobile first).
- HTML5 markup.
Version 4 of Twitter Bootstrap has been released, but at the time of writing (January 2019), development of a version for Drupal Bootstrap has been planned, but it is not available yet.
Bootstrap is compatible with the latest versions of the Chrome, Firefox, MSIE, Opera and Safari browsers. It may not render pages correctly in some older browsers.
 Older
browsers may not render certain Bootstrap components, or render them different from modern browsers.
For an overview over what is supported, see the official Bootstrap documentation:
Browser and device support.
Older
browsers may not render certain Bootstrap components, or render them different from modern browsers.
For an overview over what is supported, see the official Bootstrap documentation:
Browser and device support.
Bootstrap is specifically designed to support responsive web design. This means the layout of web pages adjusts dynamically, taking into account the characteristics of the device used (i.e. desktop computer, tablet, smartphone).
Installation
The version of jQuery in the Drupal 7 core is 1.4.4. The Bootstrap framework requires a minimum jQuery version of 1.7, but not 2.0 or higher. The preferred method to accomplish this task is to install the jQuery Update project. This allows you to set local version and also to select an external CDN (such as Google) for an even newer version.
So, before installing, make sure you have jQuery update enabled:
$ drush en jquery_update -y
Then, configure it as follows
- Set the "Default jQuery Version" to the latest (e.g. 1.10).
- Set "Alternate jQuery version" to 1.5 (This prevents issues with AJAX-heavy modules like Views).
- Set jQuery compression level to minfied unless you're debugging jQuery.
- You may want to set up a CDN (Content Delivery Network) such as Google to serve jQuery directly to your users from Google's network of datacenters. (Doing so will allow the CDN-provider to bypass cross-domain security.)
The screenshot below shows the settings I use:

After setting up jQuery update, you should
download and enable the Bootstrap theme and place it in the
customary place for Drupal themes
(i.e. sites/all/themes). The
following drush-command will do that:
$ drush en bootstrap -y
Then, set Bootstrap as the default theme. Make sure you are logged in as an administrator, and in the black administraton menu at the top of the screen, press “Appearance”. Then set Bootstrap as the default theme, and disable Bartik.
After you enable it, you will find that it has a few settings that can be adjusted in the Bootstrap GUI. While well suited to serve as a starter or base theme, Drupal Bootstrap also works reasonable well on its own for projects where you just want a basic responsive website.
However, if you want to customize the look and feel of the site, you need to create a sub-theme.
Creating a sub-theme
The official documentation for creating a Bootstrap sub-theme is on the Drupal Bootstrap website. (The user contributed documentation at Drupal.org is obsolete.) You may also want to read the official documentation at the Bootstrap home site (links in top bar).
Before proceeding, note that there are two different ways to sub-theme Bootstrap:
- Bootstrap CDN: This is the simplest method. It utilizes CDN Bootstrap as a base theme, but will allow you to override existing CSS styling (but without the power of less) in the sub-theme and alter the PHP templates.
- Bootstrap less source files:
This method is the most dynamic and will grant you the ability to change the variables and utilize the mixins provided by Bootstrap using the CSS pre-processor less.
It entails downloading and extracting the latest Bootstrap source into your sub-theme and place it in a folder named
bootstrap, and then copying and modifying some of them as described below.
To create a sub-theme (we are going to call
it mybootstrap in this example) for your customisations
of Bootstrap, you start out by performing these steps:
- Recursively copy all the files from the
bootstrap/starterkits/THEMENAMEtomybootstrap. If you're posititoned in thethemesdirectory, andmybootstrapdoes not exist, you may use this command:$
cp -R bootstrap/starterkits/THEMENAME mybootstrap - In the
mybootstrapdirectory, rename fileTHEMENAME.starterkittomybootstrap.info. - Edit
mybootstrap.infoto give it a more suitable name and description. - To use Bootstrap Less source files, also modify
mybootstrap.infoas follows:- Uncomment the appropriate JavaScript entries to enable the assets provided by the Bootstrap Framework. (Do not uncomment the lines that apply to Sass,)
- Uncomment the line:
settings[bootstrap_cdn_provider] = ''(at the bottom). This makes sure that the CDN Provider is automatically disabled when your sub-theme is installed:
Bootstrap CDN
It is claimed that using a CDN to deliver client side scripts directly to the browser has several advantages over delivering it from your server: decreased latency, increased parallelism, and better caching. However, using a CDN also has security implications, such as:
- The CDN can be hacked, or it may deliberately alter scripts to inject malicious code.
- The CDN can determine what pages is visited on your site.
- If the SSL Certificate of the CDN is not recognized by the client, some parts of your site will suddenly not work for these clients (very hard to debug).
Using a Bootstrap CDN is best suited for testing and for experimental projects. Using a CDN for a production site is deprecated.
To set up the Bootstrap CDN method, navigate to , and make sure “CDN Provider” is not set to “- None -”.
If you choose this method, you don't have to do anything else, unless you wish to override the default Bootstrap base theme settings.
If you want to do this, copy the settings you want to change from
the base theme into the sub-theme's .info-file. You may
also edit the provided css/style.css with your overrides
and alter the PHP templates that controls page and entity layout.
Working with the Bootstrap less source files
 To
work with the Bootstrap source files, you'll need the less compiler
(lessc). If tool this is missing from your environment, you must
first install it. Getting the required tools in place is
not described here, but you want to refer back to the
to webmaster's notes to learn how to install lessc on a web server.
To
work with the Bootstrap source files, you'll need the less compiler
(lessc). If tool this is missing from your environment, you must
first install it. Getting the required tools in place is
not described here, but you want to refer back to the
to webmaster's notes to learn how to install lessc on a web server.
To use the Bootstrap less source files, you need to download the latest version of the Bootstrap 3 source code (seems settled at ver. 3.4.1, but check the version pulldown menu to make sure), or copy them from an existing Bootstrap subtheme you may have.
To copy, just copy the following two subdirectories in your subthemes root directory:
bootstrap/less/
To download boostrap, click on the “Download bootstrap” button and
download the version of the library you want and place it inside your
sub-theme folder. There are three different download options, but the
one you want is the one called “Source code”. The zip file will
unpack to a directory where the version number is part of the name.
Rename this directory to bootstrap after unpacking (this
means it will be:
mybootstrap/bootstrap).
Next, to get the less files for Drupal, download
Drupal Bootstrap Styles
and locate the less subdirectory (src/3.x.x/7.x-3.c/less).
Copy it into the top directory of your subtheme, giving you
mybootstrap/less).
You should now be able to do the following to generate the stylesheet from your site based upon the less source files (the syntax >| overrides the noclobber setting):
$ lessc less/style.less >| css/style.css $ drush cc theme-registry
There should be no error messages (you may get the warning “(node:5171) [DEO0026] DeprecationWarning: util.print is deprecated. Use console.log instead.”), and the file
css/style.css should have more than 7000 lines of
css.
 Until
you generate
Until
you generate css/style.css and flush the theme registry
cache, the newly created sub-theme will appear unthemed.
Here is a rundown of what is in mybootstrap/less:
- The file
bootstrap.lessis a version of the file with the same name in the the Bootstrap source file library. It imports all the other source file and is just changed so that the path points to the same file. It also importsvariable-overrides.lessafter the originalvariables.less, so that variable overrides will take precedence. Generally, we will not need to modify this file unless there is a requirement to add or remove imported files. - The file
drupal-bootstrap.lessfiles contains more than 800 lines CSS classes that is added to make the Drupal version of the theme work as a regular theme. - The file
variable-overrides.lessis for your varaiable overrides. Out of the box, there is just a single override: The@icon-font-pathis set to point to the directory containing glyphicom halflings. It is this file you will use most of the time when you adapt your Bootstrap sub-theme. To customize Bootstrap settings, it is better to change a variable than to override css. - The file
style.lessis the glue that holds it all together. Initially, it importsbootstrap.less(which imports all the bootstrap source files and the variable overrides), anddrupal-bootstrap.less. Compiling this with lessc will and put everything into one file. You may add one or more imports to this to hold your custom css.
You are expected to put your variable overrides
in variable-overrides.less. However you should not add
your own CSS overrides to drupal-bootstrap.less, as this file
may change if Drupal Bootstrap Styles is updated.
Instead you may either place your own css overrides in a single
separate file (e.g. custom.less), or you split custom css
for header, content, footer, etc. in separate less files, such as:
header.lesscontent.lessfooter.less
After adding your own files to the sub-theme, make sure you import
them in style.less.
The overall directory structure should look similar to this when you're done:

 Note
that the only folders you shall need from the bootstrap source
are
Note
that the only folders you shall need from the bootstrap source
are fonts, js and less (located
directly inside the bootstrap directory). The materials
in the dist, docs , grunt and any other directories
that may appear are not used, but may be referred to as documentation,
examples or backup copies. It is safe to delete these, and you should
do so on a production site. If you use Bootstrap as a starter theme,
you can get rid of the entire bootstrap directory by moving fonts, js
and less to new locations under your sub-theme. Remember
to update all internal references if you do this.
If you use Scald for media management, refer to the section about Adding contexts to learn about some recommended CSS tweaks for the Scald image contexts.
Copy templates into the sub-theme
After having installed the Bootstrap theme and created a sub-theme, you may want to alter the latter to make its visual appearance more appealing. This chapter will not provide a full tutorial on how to customize a Drupal sub-theme, but will provide some pointers to get you started.
Generally, there are four things you can tweak to alter how your sub-theme looks:
- CSS – to override defaults and add custom classes, edit
css/style.css(Bootstrap CDN) or less source files (if you're using Bootstrap less source files). template.php– this is a file where you may place pre-process functions and theme function overrides*.tpl.php– template files consists mainly of semantic HTML5 (referencing CSS-classes for layout) and PHP print-statements to print variables passed to the template by pre-process functions. Avoid putting PHP logic in the template. Instead perform logic operations in a pre-process function.*.info– specifies regions, and need to be coordinated with the regions actually used in template files.
If you need to override the template files, you need to copy those
you alter to the directory
themes/bootstrap/templates/ in your sub-theme
(e.g, themes/mybootstrap/templates). Here is where to find those
it is most likely you want to alter in the Bootstrap base theme:
node.tpl.php(in sub-directorynode)page.tpl.php(in sub-directorysystem)html.tpl.php(in sub-directorysystem)
The Drupal Bootstrap theme does not include a
template for comments (comment.tpl.php). This means the
version of this template in core is used. If you need to modify this,
the file to copy is
modules/comment/comment.tpl.php.
 Along
with the templates
Along
with the templates page.tpl.php
and html.tpl.php are files containing pre-process
functions for these templates. These files have names ending
with .vars.php (e.g. page.vars.php). Do not
copy these files along with the template to your subtheme (if you do,
your site will crash because the bootstrap pre-process functions will
be loaded twice). If you need your own pre-process function, prefix
them with the name of your sub-theme and place them in your
own .vars.php-files or in your
sub-theme's template.php.
You should now set your subtheme as the default theme. Click on “Appearance” in the black administration menu and enable and set default your subtheme. You should not disable the Bootstrap base theme (it works with it disabled, but that is just because of a bug in Drupal).
Main menu
The Bootstrap default menu behaviour does not auto-expand a menu on hover. It works as a click on the top level to expand. This works well on mobile platforms where hover is not available.
In your menu settings page, enable “Show as expanded” for the parent item of the menu items you want to appear in the dropdown.
If you need a dropdown on hover, use the Superfish bridge project to enable the jQuery Superfish plugin.
Bootstrap GUI
Before drilling down into CSS, it may be a good idea to explore the settings the Drupal Bootstrap bridge module let you change in the GUI. It may save you from creating a lot of custom CSS for your site.
To explore the GUI, navigate to for your Bootstrap sub-theme, you'll find a page with the heading “Bootstrap settings”. The vertical tab has the following four components:
- General
- Components
- JavaScript
- Advanced
Below are some brief notes about using these. [This should be expanded, but it has to do for now.]
General
The general settings establish some defaults for styling of the content elements listed below.
The “Forms” setting let you use the .has-error class to highlight required fields in empty entry forms.
If you set this you may want to untick the corrosponding setting under the “JavaScript” vertical tab.
- Container: Use the “Fluid container” class. See the section about Layout below to learn what this means.
- Buttons: Size and other options for buttons.
- Forms: Alter use of the error class (see: “JavaScript » Forms” below).
- Images: Select default image shape and toggle responsive images.
- Tables: Style settings for tables.
Of these, enabling responsive images is the most useful one. Doing
so will automatically add the img-responsive class to
images with max-width: 100%; and height:
auto;. This will make the image scale nicely relative to the
parent element.
Components
The settings for components also establish some defaults for styling of the components listed below.
- Breadcrumbs: Set how to show breadcrumbs.
- Navbar: Set Navbar position and style.
- Pagination: Show “First” and “Last” links in the pager.
- Region wells: Enable the well-classes for specified regions.

The Drupal Bootstrap theme let you put any regions in well through the GUI. To do or undo this, navigate to and use the pull-down meny for the region. The screenshot below show that the Primary region is placed in a well through the GUI.
JavaScript
The settings for JavaScript let you alter the use of error class in forms and improve performance by disabling popovers and tooltips.
- Anchors: Advisory text.
- Forms: Alter use of the error class (see: “General » Forms” above). Enable smart form descriptions (via ToolTips).
- Popovers. Enable and set options for popovers (may impact performance).
- Tooltips. Enable and setting options for tooltips (may impact performance).
If the tooltip is enabled, field descriptions will be displayed as Bootstrap tooltips. The example below shows the username field:

If you disable the tooltip, field descriptions will be displayed as plain text below the field:
Advanced
IMHO, these setting are not “advanced”. Only change them from the default if there is a good reason.
- Checkbox to supress jQuery version error message if you don't use jQuery Update.
- CDN: Let you set a CDN Provider. If you're working with less source files for the CSS, you must set this to “- None -”.
Layout
Please see original documentation.
The following diagram shows the structure of the default layout of the page.tpl.php
that ships with Bootstrap.
<header id="navbar">
<div class="container">
<!-- logo, name and navbar -->
</div>
</header>
<div class="main-container container">
<header id="page-header">
<!-- slogan -->
</header>
<div class="row">
<aside class="col-sm-3">
<div class="region region-sidebar-first">
</div>
</aside>
<section class="col-sm-X">
<div class="region region-content">
</div>
</section>
<aside class="col-sm-3">
<div class="region region-sidebar-second">
</div>
</aside>
</div>
</div>
<footer>
</footer>
Below is what is measured by inspecting the layout with a fixed grid. For each element the following values are recorded for the horizontal dimension: margin+padding+content.
- header#navbar: auto+30+1110
- main-container: auto+30+1140
- header#page-header: 0+0+1140
- row: -30+0+1170
- No sidebars:
- section: 0+30+1140
- total:1170
- Both sidebars:
- aside1: 0+30+262.5
- section: 0+30+555
- aside2: 0+30+262.5
- total:1170
- footer: auto+30+1140
Tweaking the layout
Moving header#page-header inside the outmost container
of header#navbar works as one would expect, and puts the
site slogan in the position most people would expect to find it.
<header id="navbar">
<div class="container">
<!-- logo, name and navbar -->
<header id="page-header">
<!-- slogan -->
</header>
</div>
</header>
…
To change the header to span the full width of the screen, you may
either, set the “Fluid container” class in
the GUI, or you may wrap it in
a <div> of the class “container-fluid” as shown below.
<div class="container-fluid">
<header id="navbar">
<div class="container">
<!-- logo, name and navbar -->
<header id="page-header">
<!-- slogan -->
</header>
</div>
</header>
<div>
…
The same technque works for making the footer span full width.
If you change this in the GUI, the navbar and footer will be in a fluid container that spans the full screen. If you use a wrapper, they will be in fixed size containers and only the decoration (e.g the header and footer background colour will span the full screen width.
Grid
Bootstrap provides a responsive, mobile first fluid grid
system built around 12 columns. Using a single set
of .col-md-* grid classes, you can create a basic grid
system that starts out stacked on mobile devices
before becoming horizontal spanning all 12 columns on desktop screens. It
includes predefined
classes for layout, as well as
less mixins for generating semantic layouts.
The fixed grid layout by default assumes a total width of 1200px (i.e. 100px/column). You may override this by navigating to and checking the box for “Fluid container”, which provides a full width fluid layout.
The page.tpl.php template that comes with
Drupal Bootstrap set up 3 regions side-by-side in the
main page area.
To enable or disable sidebars, navigate
to . The width of both
sidebars are fixed for screens larger than the small size (768px). It
is set to is set to 3 columns (col-sm-3)
in page.tpl.php. The class to use for “Content” column
(content_column_class) is computed in the page
pre-process function bootstrap_preprocess_page() (located
in page.vars.php). The default computation assumes that
each of the sidebars are 3 columns wide. If you use sidebars and
override the width of either sidebar in the page template for your
subtheme, you need provide your own page pre-process function in
template.php.
The example is below is just a copy of the original function, with
comments added. It assume both sidebars are set up with the
class col-sm-3 in page.tpl.php
and compute the class to use for the content_column_class
for three cases: Both, one or none of the sidebars populated.. If you
instead use col-sm-2 for the sidebars, the
content_column_class should be
col-sm-8,
col-sm-10 or
col-sm-12 respectively.
// Assuming both sidebars are col-sm-3
function mybootrap_preprocess_page(&$variables) {
// Add information about the number of sidebars.
if (!empty($variables['page']['sidebar_first']) &&
!empty($variables['page']['sidebar_second'])) {
// Both: 12 - 3 - 3 = 6
$variables['content_column_class'] = ' class="col-sm-6"';
}
elseif (!empty($variables['page']['sidebar_first']) ||
!empty($variables['page']['sidebar_second'])) {
// One: 12 - 3 = 9
$variables['content_column_class'] = ' class="col-sm-9"';
}
else {
// None: 12 = 12
$variables['content_column_class'] = ' class="col-sm-12"';
}
}
If any of these assuptions change, you need to override this
function in your subtheme's template.php. For instance:
If the number of columns preset for the sidebars change, this must be
taken into account when computing
the content_column_class, If the page template breaks
on col-md instead col-sm,
the content_column_class must be of the same type.
Regions
The position of the default 8 block regions defined by Drupal Bootstrap is shown below:

The default logo is 32 x 32 px.
Steps to create a modern front page
Modern web design do not use sidebars on the front page.
- By default, the blocks “Search form”, “Navigation” and “User login” are in the “Primary” region (left sidebar). Remove all blocks from “Primary” region.
- Remove “Powered by Drupal” from “Footer” region.
Responsive layout
A responsive grid system, where the display respons to the screen size, is in the DNA of Twitter Bootstrap.
 See
also the original Bootstrap documentation:
Media queries.
See
also the original Bootstrap documentation:
Media queries.
The breakpoints for media queries are defined
in variables.less, astarting round line 283. For Bootstrap 3, they are:
@screen-xs-min: 480px;// Extra small (deprecated) @screen-sm-min: 768px; // Small @screen-md-min: 992px; // Medium @screen-lg-min: 1200px; // Large
When creating responsive pages, the default should be for mobile devices (i.e. devices with screen width < 768px), then create overrides for larger devices.
For example, the CSS below will by create a rule where
the logo class by default don't display (we usually want
this for mobile devices), but if the screen width ≥ 768px, it will
display as a block.
.logo {
display: none;
@media (min-width: @screen-sm-min) {
display: block;
}
}
Bootstrap comes with four types of class prefixes for creating columns for different size displays:
col-xsfor extra small displays (screen width < 768px).col-smfor small displays (screen width ≥ 768px).col-mdfor medium displays (screen width ≥ 992px).col-lgfor large displays (screen width ≥ 1200px).
 The
class prefix
The
class prefix col-xs is not deprecated, even if the variable
@screen-xs-min is.
The proper use of the grid is to use it to create responsive blocks in a sub-theme. However, the grid can be used everywhere, including inside Drupal components such as an Article node. Below is an example that demonstrates the use of the grid in this context.
Following the prefix is the number of columns (from 1 to 12) to use
for the div-container. I.e. col-xs-12 request that all
12 colums are used for the container on extra small displays.
To see it in action, create an article node with the following markup in the body:
<div class="container">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-xs-12 col-sm-6 col1">
<h4>Column 1</h4>
</div>
<div class="col-xs-12 col-sm-6 col2">
<h4>Column 2</h4>
</div>
</div>
</div>
Make sure you set the text format to "Full HTML", otherwise the markup will be stripped and the CSS classes will have no effect.
When we specify the class col-xs-12 col-sm-6, it means
the element should span all 12 of the available Bootstrap columns on
extra small screens, but only 6 columns on small displays and larger.
You may want to see how this works by viewing this node on displays of
different width.
Please note that this is just a demonstration. The CSS classes
that create columns is not
supposed to be used inside Drupal nodes. The proper use of such CSS is inside a page
template (e.g. page.tpl.php) to create responsive page
layouts.
A CSS media query is an expression of some media feature that resolves in either true or false. When a media query is true, the corresponding style sheet or style rules are applied.
Class names for hiding stuff, or making it visible as a block:
hidden-xs visible-xs-block hidden-sm visible-sm-block hidden-md visible-md-block hidden-lg visible-lg-block
Se also: StackOverflow: Hiding elements in responsive layout.
Colours
Bootstrap defines five shades of grey (using the US-spelling “gray”) and five “brand” colours in variables.less:
//== Colors // //## Gray and brand colors for use across Bootstrap. @gray-base: #000; @gray-darker: lighten(@gray-base, 13.5%); // #222 @gray-dark: lighten(@gray-base, 20%); // #333 @gray: lighten(@gray-base, 33.5%); // #555 @gray-light: lighten(@gray-base, 46.7%); // #777 @gray-lighter: lighten(@gray-base, 93.5%); // #eee @brand-primary: darken(#428bca, 6.5%); // #337ab7 curious blue @brand-success: #5cb85c; // fern green @brand-info: #5bc0de; // viking blue @brand-warning: #f0ad4e; // faded orange @brand-danger: #d9534f; // roman red
The descriptive colour names above are derived from Name that colour. I believe this provides the most descriptive names. Alternative sites that uses different names for colours are colorpedia and HTML CSS color picker. Additional descriptive colour names that are understood by most modern browsers can be found here: HTML Color Names.
The default main text colour in Bootstrap is @gray-dark.
The diagram below shows the five “brand” colours defined in Bootstrap, as well as regular web orange (#ffa500).

@brand-primary is used as background for the search icon, etc.
Bootstrap components and helper classes
Below are a list of the components and helper classes that you may want to use when creating content on a website that builds upon the Bootstrap framework. It is derived from the the original documentation on the Bootstrap website.
Alerts
Please see original documentation.
Badges
Please see original documentation.
Breadcrumbs
Please see original documentation.
Button dropdowns
Please see original documentation.
Button groups
Please see original documentation.
Carousel
Please see original documentation.
Clearfix
Bootstrap's clearfix helper class is can be used to clear floating elements.
It is based upon the micro clearfix hack popularized by Nicolas Gallagher. Example:
<div class="clearfix"></div>
Dropdowns
Please see original documentation.
Glyphicons
Please see original documentation.
Bootstrap includes over 250 glyphs in font format from the Glyphicon Halflings set. To use one of these you use a span with the glyphicon class and another class naming the symbol.
For example, to render the power off-symbol, you use the following:
<span class="glyphicon glyphicon-off"></span>
There is a chart showing the glyphs available in Bootstrap and their classes at the Bootstrap website.
To change size for all glyphicons:
.glyphicon {
font-size: 50px;
}
To target only one glyphicon:
.glyphicon.glyphicon-calendar {
font-size: 75px;
}
 Note
that both the names and the markup differs from the Bootstrap Glyphicon Halflings available on
GitHub.
Note
that both the names and the markup differs from the Bootstrap Glyphicon Halflings available on
GitHub.
 Glyphicons Halflings
are normally not available for free, but their creator has made them
available for use with Bootstrap at no cost. As a thank you, you
should consider including a link back
to Glyphicon in your footer,
colophon, “Thanks”-page, or similar.
Glyphicons Halflings
are normally not available for free, but their creator has made them
available for use with Bootstrap at no cost. As a thank you, you
should consider including a link back
to Glyphicon in your footer,
colophon, “Thanks”-page, or similar.
Input groups
Please see original documentation.
Jumbotron
Please see original documentation.
Labels
Please see original documentation.
List group
Please see original documentation.
Media object
Please see original documentation.
Navbar
Please see original documentation.
Navs
Please see original documentation.
Page header
Please see original documentation.
Pagination
Please see original documentation.
Panels
Please see original documentation.
Panels are used to display text or images within a box with rounded corners. It may optionally include a header or a footer. Sample markup;
<div class="panel panel-danger">
<div class="panel-heading">
ATTENTION
</div>
<div class="panel-body">
Lorem ipsum dolor sit ametnim ...
</div>
<div class="panel-footer">
<a href="#" class="btn btn-danger btn-sm">Danger</a>
<a href="#" class="btn btn-warning btn-sm">Warning</a>
<a href="#" class="btn btn-success btn-sm">Success</a>
<a href="#" class="btn btn-primary btn-sm">Primary</a>
<a href="#" class="btn btn-info btn-sm">Info</a>
<a href="#" class="btn btn-default btn-sm">Default</a>
</div>
</div>
The above markup will divide the panel into three parts: the panel-heading, panel-body and panel-footer.
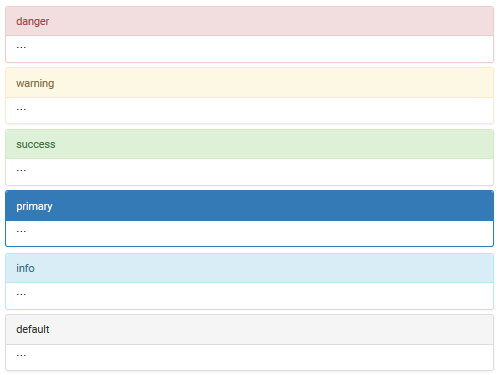
As is you can see, panels come with various colour options for buttons. Similar classes exist for the panel as well. These classes go in the panel container, but apply to the panel-heading background.
panel-dangerpanel-warningpanel-successpanel-primarypanel-infopanel-default
The names of the colours that are part of the class-names for
panels and buttons are similar to those defined
as colour brand variables above, but the
colors are not the same. Those for panel-heading background
(except panel-primary) are much lighter than the brand
colours.
There are no Bootstrap classes for colouring the panel body and footer, but you may do it by adding your own cascade to the classes for these panel components. Example:
.panel-body,
.panel-footer {
background-color:@brand-success;
}
Progress bars
Please see original documentation.
Responsive embed
Please see original documentation.
To make an image responsive (i.e. it will always be downsized to
fit in its container, you may use the
class img-responsive. Note that this have a performance
penalty on a small screen, because the large image is downloaded and
then scaled down on the client side.
Thumbnails
Please see original documentation.
Images and videos in Bootstrap are usually referred to as
“thumbnails”. Embedding it in a <div> with
the thumbnail class will put a frame around the image.
For best effect, use an image that is the same size as the container
object.
Here's an example of the markup to use for creating a thumbnail with a caption:
<div class="thumbnail"> <img src="…"> <div class="caption">Caption.</div> </div>
The default is that thumbnails are centered.
For left-aligned thumbnails, use the class pull-left.
For right-aligned thumbnails, use the class pull-right.
However, by default, only centered thumbnails are responsive.
For videos and slideshows, there is
the embed-responsive class. It allows the browser to
determine video or slideshow dimensions based on the width of their
containing block by creating an intrinsic ratio that will properly
scale on any device.
<div class="thumbnail embed-responsive embed-responsive-16by9"> <iframe class="embed-responsive-item" src="…"></iframe> </div>
The example above is for 16:9 aspect ratio. For 4:3 aspect ratio embed-responsive-4by3.
Remove the attributes giving an explicit width and height. You may also remove
frameborder="0" in your <iframe>s as this is overridden by these classes.
These classes can be used to wrap <iframe>, <embed>, and <object> elements;
optionally use an explicit descendant class .embed-responsive-item when you want to match the styling for other attributes.
Tooltips and popovers
A Bootstrap tooltip is a small floating message that by default appears when the mouse is hovered over a component in a website. It is often used to display help text for a particular component.
Please see original documentation for full set of attributes.
Bootstrap's tooltip is made by means of CSS and triggered by means of JavaScript. It is fairly lightweight compared to many other tooltip plugins.
Here is an example a tooltip with a button as its parent component:
<button type="button" class="btn btn-lg btn-success" data-toggle="tooltip" data-placement="top" title="This is a Bootstrap tooltip.">Hover over me </button>
Drupal Bootstrap automatically uses tooltips for field descriptions if it is enabled.
A Bootstrap popover is a small overlays of content, that can be added to any element for housing secondary information.
Please see original documentation for full set of attributes.
<button type="button" class="btn btn-lg btn-danger" data-toggle="popover" data-placement="top" data-trigger="focus" title="Popover title" data-content="Here is some content.">Click to toggle popover </button>
The tooltip or popover is defined by setting the attribute data-toggle to tooltip or popover.
There are also an option to position the effect with respect to its parent component (top, bottom, right, and left),
by means of the attribute data-placement.
To enable tooltips or popovers, visit the JavaScript vertical tab of the GUI. Neither will appear unless enabled. The GUI also let you provide some defaults for placement and triggering.
Wells
Please see original documentation.
A well is a container that causes the content to appear i a shaded box with rounded corners that make it appear sunken on the page.
To create a well, simply wrap the content that you would like to
appear in the well with a <div> containing the
class well. The following example shows a very basic
well, used to display a TOC of a node with inline links.
<div class="well pull-right">
<h4>TOC</h4>
<ul>
<li><a href="#htekst">Hypertext</a><ul>
<li><a href="#lenker">Links</a></li>
</ul></li>
<li><a href="#tech">Techniques</a></li>
<li><a href="#littl">Sources</a></li>
</ul>
</div>
You can change the size of well using the optional classes such as,
well-lg or well-sm. These classes are used
in conjunction with the well class. These classes
affect the padding, making the well larger or smaller.
<div class = "well well-lg">I am in large well.</div> <div class = "well well-sm">I am in small well.</div>
Inline form elements
By default, Boostrap increases an input field to the full width of the container. (see this section to learn how to override this).
As noted
in this
issue, fields 'color', 'date', 'number', 'range', 'tel',
'weight' are exempted.
To make other fields inline, create a wrapper-div and
set the class of this wrapper
to form-inline. Example:
function example_form($form, &$form_state) {
$form['example_info'] = array(
'#markup' => t('Arrival and departure'),
);
$form['container'] = array(
'#prefix' => '<div class="form-inline">',
'#suffix' => '</div>',
'arr' => array(
'#title' => t('Arrival:'),
'#type' => 'textfield',
'#size' => 14,
),
'dep' => array(
'#title' => t('Departure:'),
'#type' => 'textfield',
'#size' => 14,
),
);
return $form;
}
Updating Bootstrap
On a Drupal site, Bootstrap are made up of two or three components:
- The Drupal Bootstrap base theme.
- The Twitter Bootstrap less source files.
- The Drupal Bootstrap Styles less source files (if you're using less).
All of these may need updating.
Updating the Bootstrap base theme
If you've followed the instructions above and made all your changes to Bootstrap in a sub-theme, you should be able to update without overwriting your changes with the following drush command:
# drush dl bootstrap
Bootstrap is a theme and does not use the database, so there is no need to worry about schema-updates.
After installing the new version, compare the regions set up
in THEMENAME.starterkit with those defined
in mybootstrap.info
Updating the Twitter Bootstrap less source files
The file named bootstrap/_config.yml (located in your
sub-theme) will tell you the version of Twitter Bootstrap currently installed).
If this is not the latest version of the Bootstrap 3 branch, you should update.
- Download and unpack the latest version of the Bootstrap source code in the top directory of your sub-theme. It will unpack to a directory where the version number is part of its name.
- Rename the existing
bootstrapsub-directory in your sub-theme tobootstrap_old. - Rename the unpacked sub-directory (having its version number as part of its name) to
bootstrap. - Compare the versions in your sub-theme of
less/bootstrap.lessinbootstraptobootstrap_old. If it has changed (except for comments), you may need to editless/bootstrap.lessused by your subtheme to reflect the changes. - After making these edits (if required), you should delete the
bootstrap_olddiretory and its contents.
Updating Drupal Bootstrap Styles
The styles that live in the less subdirectory of your subtheme
are maintained as a separate
Drupal Bootstrap Styles
project on GitHub.
This may be updated, in particular if the
Drupal Bootstrap bridge project is updated. Provided
you've kept your own styles in separate files, just stash your own
styles and
variable-overrides.less, install the new version and restore your changes.
Quirks
This sections describes quirks you may experience when Bootstrap is used as the theme on a Drupal 7 website.
Maintenance template ignored on frontpage
The Drupal Bootstrap theme comes with a
maintenance page template
(templates/system/maintenance-page.tpl.php).
However, this is ignored in the front page. To get it noticed, have
the following in the subtheme's template.php, in
THEME_preprocess_page():
if (drupal_is_front_page()
&& !user_has_role(3, $account = NULL)
&& variable_get('maintenance_mode') == 1) {
$variables['theme_hook_suggestions'][] = 'maintenance_page';
}
Source: ShaneMcGovern's sandbox@Drupal.org.
Size of textfield
When adding a field to a content type, one of the settings is “Size of textfield”. Setting this has no effect when Bootstrap is used as the theme because Bootstrap, by default, increases the size of an input to the full width of the container. (The “Size of textfield” seeting works as one would expect in Bartik and most other themes.)
When Bootstrap is used as the theme, you must use css to control the size of a textfield. Example:
#edit-arrival,
#edit-departure {
width: 10em;
}
Book
By default, Bootstrap replaces the core book
nevigation menu with a pull-down menu with the heading “Outline” at
bottom right. Placing the following hook in the
sub-theme's template.php resets book navigation back to
what core provides.
/**
* Implements hook_process_HOOK().
*/
function MYSUBTHEME_process_book_navigation(&$variables) {
// Reset book navigation back to what core provides.
template_preprocess_book_navigation($variables);
}
Source: Drupal.org: Book Navigation Support.
Final word
From experience, I've learned that Bootstrap does not work well with Safari version 5 and MSIE version 8 (and older). Until 2014, to make pages look less broken in older browsers, you could invoke Chrome Frame:
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=Edge,chrome=1">
However, as noted in this statement on the Chromium blog, today, most people run modern browsers, and this type of hack should no longer be used.
 This
tutorial has just scratched the surface. To learn more about site building and theming with Bootstrap it is strongly recommended that you visit
the official Drupal Bootstrap Documentation site. There is also a
good blog post by Thai Yin about Drupal Bootstrap Subtheming with LESS.
This
tutorial has just scratched the surface. To learn more about site building and theming with Bootstrap it is strongly recommended that you visit
the official Drupal Bootstrap Documentation site. There is also a
good blog post by Thai Yin about Drupal Bootstrap Subtheming with LESS.
Last update: 2019-05-11 [gh].